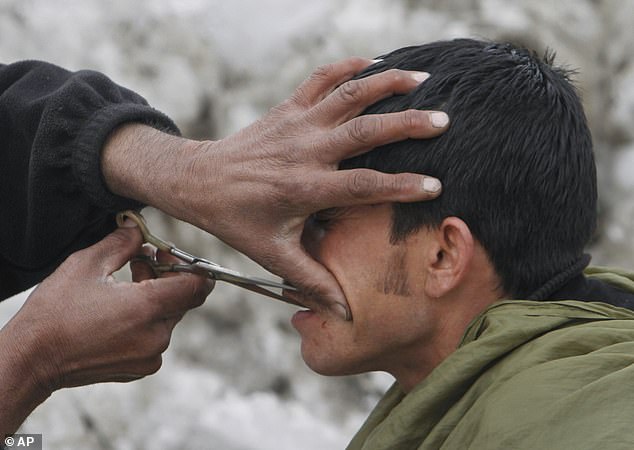
The Taliban‘s morality police have detained men and their barbers over hairstyles, and others for missing prayers at mosques during Ramadan, a UN report has said.
It comes six months after laws regulating people’s conduct in the country came into effect.
The Vice and Virtue Ministry published laws last August covering many aspects everyday life in Afghanistan, including public transport, music, shaving and celebrations.
Most notably, the ministry issued a ban on women’s voices and bare faces in public.
That same month, a top UN official warned the laws provided a ‘distressing vision’ for the country’s future by adding to existing employment, education, and dress code restrictions on women and girls.
Taliban officials have rejected UN concerns about the morality laws.
Thursday’s report, from the UN mission in Afghanistan, said in the first six months of the laws’ implementation, over half of detentions made under it concerned ‘either men not having the compliant beard length or hairstyle, or barbers providing non-compliant beard trimming or haircuts’.
The report said that the morality police regularly detained people arbitrarily ‘without due process and legal protections’.

The Taliban ‘s morality police have detained men and their barbers over hairstyles, the UN said (file image of an Afghan man getting a haircut)

A member of Taliban frisks a man at a checkpoint ahead of Eid al-Fitr in Kandahar, Afghanistan, 28 March 2025

A Taliban security personnel stands guard outside the Shah-Do Shamshira Mosque during Eid al-Fitr prayers, which marks the end of the holy fasting month of Ramadan in Kabul, March 30, 2025
During the holy fasting month of Ramadan, men’s attendance at mandated congregational prayers was closely monitored, leading at times to arbitrary detention of those who didn’t show up, the report added.
The UN mission said that both sexes were negatively affected, particularly people with small businesses such as private education centres, barbers and hairdressers, tailors, wedding caterers and restaurants, leading to a reduction or total loss of income and employment opportunities.
The direct and indirect socio-economic effects of the laws’ implementation were likely to compound Afghanistan’s dire economic situation, it said.
A World Bank study has assessed that authorities’ ban on women from education and work could cost the country over 1.4 billion dollars (£1 billion) per year.
The Taliban leader, Hibatullah Akhundzada, has emphasised the primacy of Islamic law and the role of the Ministry of Vice and Virtue in reforming Afghan society and its people.
In a message issued ahead of the religious Eid Al-Fitr festival that marks the end of Ramadan, Akhundzada said it was necessary ‘to establish a society free from corruption and trials, and to prevent future generations from becoming victims of misguided beliefs, harmful practices and bad morals’.
More than 3,300 mostly male inspectors are tasked with informing people about the law and enforcing it, according to the report.
Nobody from the Vice and Virtue Ministry was immediately available for comment about the report.
This article was originally published by a www.dailymail.co.uk . Read the Original article here. .